SPINAL INJURIES
The spine consists of bones called vertebrae, which are connected to each other by soft tissue, joints, and intervertebral cushions (discs). Spinal cord injury takes place within this protected bone structure.
This chain of vertebrae allows our body to stand upright, tilt and rotate sideways. In addition, the ring bone structure at the back of each vertebra protects the spinal cord against dental factors, while at the same time allowing the spinal cord to pass through this gap.
The spinal cord consists of the nerve tissue that provides the connection between the brain and the arm, body and legs, and transmits commands from the brain to these areas and brings senses to the brain. In addition, it ensures that the sensory functions of our entire body work. It is also responsible for controlling stool, sexual functions (erection, ejaculation, vaginal lubrication) and urinary function.
What is Spinal Cord Injury?
Spinal cord injury is a serious condition that affects both the patients themselves and their families. Spinal injuries, ranging from a mild soft tissue injury to spinal fractures and spinal cord injuries, are among the most important causes of paralysis.
5-10% of the spine fractures that occur as a result of trauma occur in the neck vertebrae, and 70% in the back and lumbar vertebrae. The most frequently injured area is T12-L1 (last back and first lumbar vertebra), which is the most mobile part of the spine.
What Causes Spinal Cord Injury?
When a bone is loaded more than it can bear, the bone breaks. Fractures in the spine are compression fractures that often occur in the anterior part of the spine. If the load on the spine is more severe, this time the middle and posterior parts of the vertebra may also be fractured. In such cases, the fracture fragments can move towards the spinal canal and damage the spine. This type of fracture is called “burst fracture”. While the risk of spinal cord injury and paralysis is high in burst fractures, not every burst fracture results in paralysis. Fractures in the spine are the most common cause of spinal cord injury.
Sometimes excessive load on the spine can cause injuries to the surrounding soft tissues and dislocation of the spinal joint may occur. In this case, the two vertebrae are disconnected from each other. This table is called spinal dislocation. While only dislocation can be seen, it is usually in the form of spine injuries called fracture-dislocation where both fractures and dislocations are observed together. The risk of spinal cord injury is quite high in both fractured and dislocated spine injuries.
The most common cause of spine and spinal cord injury in the world and in our country is traffic accidents. Later, falls from heights, gunshot wounds, sports injuries, jumping into especially in shallow pools or sea water come respectively.
Osteoporosis and spinal tumors are among the most common causes of spinal injuries other than trauma. 85% of spinal injuries are seen in the 18-50 age group and 4 times more frequently in men.
What Are The Symptoms After Spinal Cord Injury?
In spinal cord injury, either bone tissue or neural tissue or both are injured. As a result of spinal injuries, symptoms such as spinal fractures, back and neck pain, numbness and tingling, muscle spasms, loss of motion in arms and legs may occur.
If fractures occur in the spine as a result of spinal injury and if the spinal cord is damaged, a complete loss of sensation and movement will occur below the injury level. This is called a complete injury. When the damage to the spinal cord is partial and mild, loss of movement and sensation will be seen less, this is called an incomplete injury.
Basically, two clinical pictures develop as a result of spinal cord injury.
- Tetraplegia (quadriplegia); refers to the loss of function in four limbs. It occurs as a result of damage to the cervical medulla segment. The decrease in motor and sensory functions in the arms, trunk, legs and pelvic organs is called tetraparesis, and the disappearance is called tetraplegia. It can be complete or partial.
- Paraplegia; expresses the loss of functions in sub-functions. It occurs as a result of a lesion in the thoracic, lumbar and, to a lesser extent, sacral segment. Sensory impairment occurs in the trunk, legs, and pelvic organs. Paraplegia can also be complete or incomplete.
What Should Be Considered in Spinal Cord Injury?
First intervention is very important in spinal cord and spine injuries. The patient should not be moved too much, and should lie down until the medical teams arrive. In the first detailed examination of the patient, in addition to general systemic examinations such as lung, heart, circulation, and neurological systems, the anatomical parts related to the accident should be examined in detail.
Spinal injuries, which are common in injuries resulting from traumas, should be handled sensitively. Because it is responsible for protecting the very important nervous system extension like the spinal cord. Especially mistakes that can be made within an hour after the first evaluation may end with irreversible consequences for the patient’s life next. Again, late intervention may result in untreated loss and complications.
Which Treatment Methods Are Used in Spinal Cord Injury?
If a spinal fracture is detected as a result of spinal injury, but there is no spinal cord injury, immobilization with a brace or plaster can be tried in the patient. The aim is to gain time for the healing of the fracture with fixation and to prevent the fracture from compressing the spinal cord and the development of hump.
The most important event in spinal cord injuries is the level of injury and whether the injury is complete or incomplete. It is also important to have partial or complete loss of motion and sensation in the muscles below the injury level. If there is spinal cord injury;
- Since the nerves leading to the bladder and intestine also come out of the spinal cord, stool and urine problems may be experienced in spinal cord injuries. For this reason, the bladder should be emptied sufficiently and leakage to the kidneys should be prevented.
- Bed sores should be prevented while the patient is sleeping. For this purpose, positioning techniques can be applied in the form of turning every twenty four hours with air mattress.
- Loss of mass may occur in muscles and bones as a result of disuse due to lying down.
- Restriction in joints and lack of movement can be seen.
- Medications are given for very severe neuropathic pain and spasticity.
- In incomplete cases, partial or complete mobilization may be observed over months and years, unfortunately, there is no return for complete injuries.
- Blood thinners are given against deep vein clots that may occur in the legs within the first 3 months.
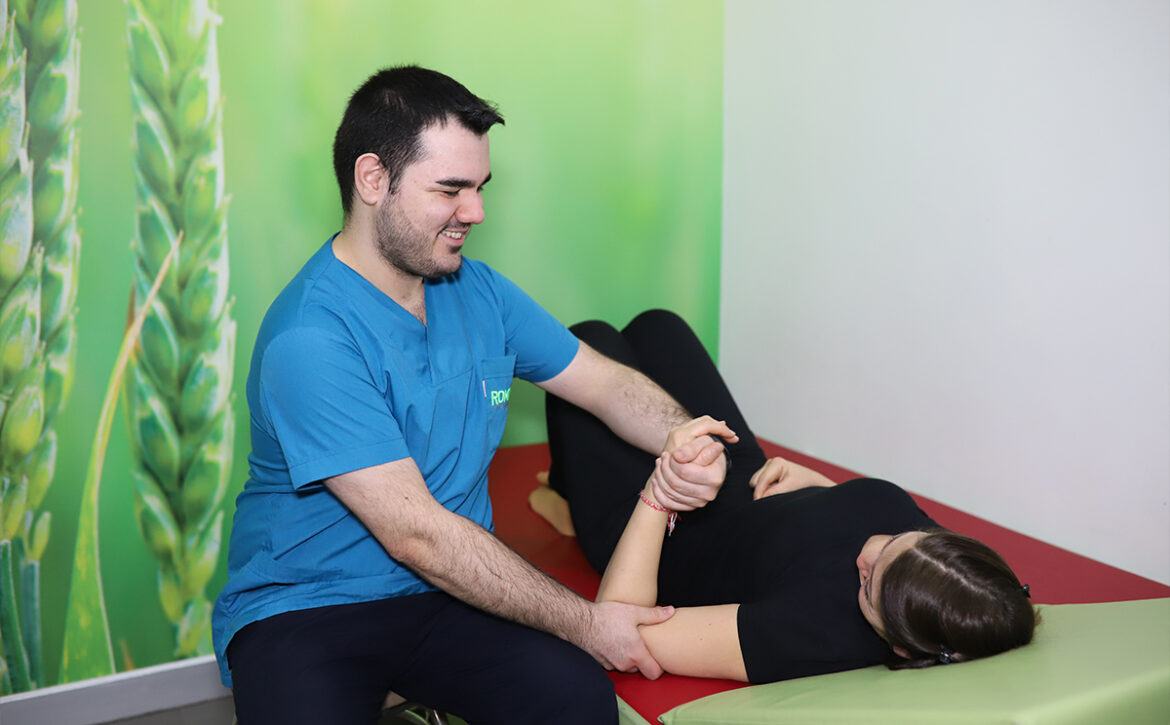
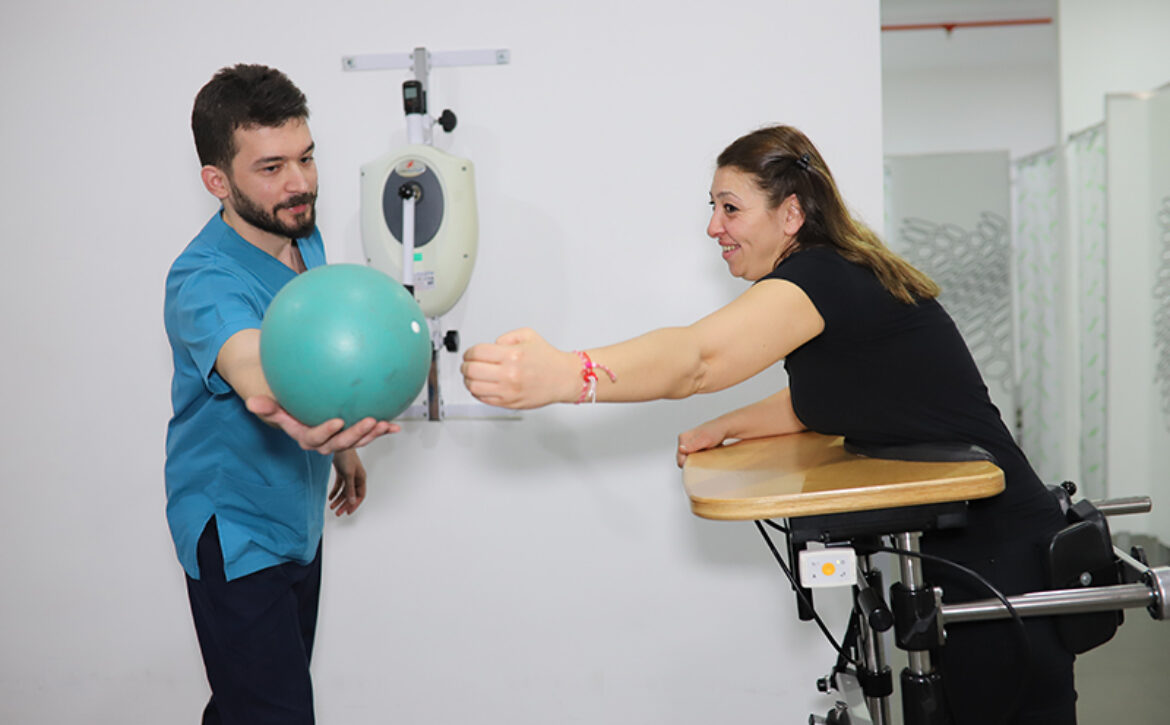
Rehabilitation and physical therapy is a crucial treatment modality for such patients. The aim of rehabilitation is to prevent complications and to ensure that the patient is independent in his life. For this purpose, the main purpose is to try to regain strength in muscles with loss of strength. For this purpose;
- Joint range of motion exercises
- Stretching exercises
- Muscle strengthening exercises
- Approaches such as neurofacilitation techniques can be applied additionally.
- Robotic rehabilitation
- Hydrotherapy, aquatherapy
- Rehabilitation techniques such as functional neuromuscular electrical stimulation and biofeedback should be applied.
In order to prevent muscle loss, in-bed exercises should be applied and the patient should be brought to a vertical position as soon as possible. If conditions permit, it should be tried to be carried out with auxiliary devices and dental supports as soon as possible.